Abstract
Background: Bortezomib or lenalidomide, in combination with dexamethasone, has been the dominant treatment option for the past decade, both in the frontline and later lines of treatment in Multiple Myeloma (MM). They have also been the comparators of choice in clinical trials of the newer generation of treatments (e.g.: daratumumab, carfilzomib, pomalidomide). Little evidence exists regarding the efficacy outcomes associated with these anti-myeloma treatments in a real-world (RW) setting.
Objective: Using RW data to characterize relapsed/ refractory MM patients receiving Rd or Vd and determine their key efficacy outcomes including overall survival (OS), treatment progression-free survival (TPFS), time-to-next treatment (TTNT) and time to treatment discontinuation (TTTD).
Methods: Patients in two RW data sources - SEER-Medicare (SM) and Optum™ integrated (OP) databases 1) with an index ICD-9 diagnosis code for MM any time from January 1, 2007 until December 31, 2013, 2) aged ≥ 18 years and 3) with no concurrent primary cancers or previously diagnosed cancers within the 365-day lookback period prior to index diagnosis were included in the study. Lines of treatment (LOTs) were identified based on business rules centered on continuity and concurrence of drug usage. In the relapsed/ refractory (i.e., LOT2+) setting, demographic characteristics were assessed, and OS, TPFS, TTNT and TTTD of the Rd and Vd cohorts were determined using Kaplan-Meier analysis.
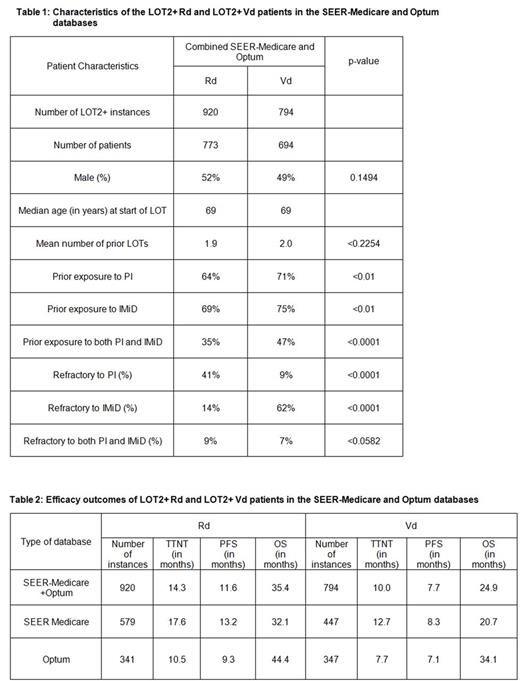
Results: In LOT2+ setting, 920 Rd (579 SM + 341 OP) and 794 Vd instances (447 SM + 347 OP) were identified. Characteristics of the two cohorts within each database are provided in Table 1. Mean age, and mean prior LOT were similar in the 2 cohorts. Prior exposure to proteasome inhibitors (PIs) differed between the cohorts (64% in Rd vs. 71% in Vd, p<0.05), as did prior exposure to immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) (69% vs. 75%, p<0.01). Sharper differences were seen in the refractoriness of these cohorts to PIs and IMiDs (PIs: 41% vs. 9%, p<0.0001, respectively, and IMIDs: 14% vs. 62%, p<0.0001). OS in the Rd cohort was 35.4 months vs. 24.9 mos in the Vd cohort, while PFS was 11.6 mos vs. 7.7 mos, TTNT 14.3 mos vs. 10.0 mos, and TTTD 10.1 mos vs. 6.3 mos (Table 2).
Conclusions: Characteristics of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma patients receiving Rd and Vd treatments differ significantly with regards to both prior exposure and refractoriness to PIs and IMiDs, which may significantly impact outcomes.
Nooka: Amgen, Novartis, Spectrum, Adaptive tecnologies: Consultancy. Voorhees: Amgen: Speakers Bureau; Oncopeptides: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy. Kumar: Celgene, Millennium/Takeda, Onyx, AbbVie, Janssen, Sanofi, Novartis, Amgen, Genentech, Merck, Oncopeptides, Roche, Skyline Diagnostics: Research Funding; Celgene, Millennium, BMS, Onyx, Janssen, Noxxon, AbbVie, Amgen, Merck, Oncopeptides, Skyline Diagnostics, Takeda: Consultancy; Skyline: Honoraria. Mehra: Janssen: Employment. Lam: Janssen: Employment. Slavcev: Janssen: Employment. Ukropec: Janssen: Employment. Potluri: Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; SmartAnalyst Inc.: Employment. Dasgupta: Janssen: Research Funding; SmartAnalyst Inc.: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal